Css Border Examples
Basic Border Styles in CSS
When creating web designs, borders are an essential aspect of styling that can significantly influence the visual impact of an element. Borders can delineate sections, highlight content, or simply add decorative flair to your webpage. In this section, we’ll explore the basics of CSS border styles, providing detailed examples and insights into how to effectively use borders in your web projects.
Understanding the Basics
Before diving into specific examples, let’s cover the basic properties that control the appearance of borders in CSS:
border-style: This property specifies whether a border is solid, dashed, dotted, or none.border-width: This property determines the thickness of the border.border-color: This sets the color of the border.
These properties can be set individually on all four sides of an element (top, right, bottom, left) or can be shorthand to apply to all sides equally.
Practical Example
Below is a complete HTML document that demonstrates various basic border styles. This example will guide you through setting different styles, widths, and colors for borders.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Basic CSS Border Styles</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
line-height: 1.6;
margin: 40px;
}
.solid-border {
border-style: solid;
border-width: 2px;
border-color: black;
padding: 20px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.dashed-border {
border-style: dashed;
border-width: 3px;
border-color: blue;
padding: 20px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.dotted-border {
border-style: dotted;
border-width: 5px;
border-color: green;
padding: 20px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.no-border {
border-style: none;
padding: 20px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="solid-border">
<p>This is a box with a solid border.</p>
</div>
<div class="dashed-border">
<p>This is a box with a dashed border.</p>
</div>
<div class="dotted-border">
<p>This is a box with a dotted border.</p>
</div>
<div class="no-border">
<p>This is a box with no border.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
A rendering of executing the code:
Explanation of the Code
- Solid Border: The
.solid-borderclass defines a solid border with a width of 2px, colored black. It’s the most commonly used border style due to its clear and straightforward appearance. -
Dashed Border: The
.dashed-borderclass is used to create a border that consists of dashes. This style is often used to draw attention or signify a separation that is less harsh than a solid line. -
Dotted Border: With the
.dotted-borderclass, the border appears as a series of dots. This style can add a playful or lighter boundary around elements. -
No Border: The
.no-borderclass sets the border style tonone, effectively removing any border from the element. It’s useful when you need to remove default borders provided by user agent stylesheets.
Border Width and Color:
In web design, controlling the width and color of borders is essential for achieving desired visual effects and enhancing user experience. CSS provides several properties to manipulate border width and color, allowing developers to customize the appearance of elements.
Border Width:
The border-width property in CSS determines the thickness of a border. It can be specified in various units such as pixels, em, rem, or percentages.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Border Width Example</title>
<style>
.border-example {
border-style: solid;
border-width: 2px; /* Set border width to 2 pixels */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="border-example">This is a bordered element with 2px width.</div>
</body>
</html>
A rendering of executing the code:
Border Color:
The border-color property defines the color of the border. It accepts color values in different formats like named colors, hexadecimal, RGB, RGBA, HSL, HSLA, or transparent.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Border Color Example</title>
<style>
.border-example {
border-style: solid;
border-width: 2px;
border-color: #ff0000; /* Set border color to red */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="border-example">This is a bordered element with red color.</div>
</body>
</html>
A rendering of executing the code:
Combining Width and Color:
Developers can combine border-width and border-color properties to achieve specific border styles tailored to their design requirements.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Combined Border Width and Color Example</title>
<style>
.border-example {
border-style: solid;
border-width: 3px; /* Set border width to 3 pixels */
border-color: #00ff00; /* Set border color to green */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="border-example">This is a bordered element with 3px width and green color.</div>
</body>
</html>
A rendering of executing the code:
Summary:
In this section, we explored how to manipulate border width and color in CSS. By utilizing the border-width and border-color properties, developers can effectively control the visual appearance of borders in web elements, enhancing the overall design aesthetics and user experience.
Rounded Borders
Rounded borders are a popular design element that can add a touch of elegance and sophistication to any web page. In CSS, you can use the border-radius property to create rounded borders. This property allows you to specify the radius of each corner of an element’s border separately.
Basic Example
Let’s start with a basic example that demonstrates how to create a rounded border. In this example, we will create a div element with a rounded border of 10 pixels.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Rounded Border Example</title>
<style>
.rounded-border {
border: 2px solid black;
border-radius: 10px;
padding: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="rounded-border">
<h1>Hello, World!</h1>
<p>This is an example of a rounded border.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
A rendering of executing the code:

In this example, we have defined a CSS class called rounded-border that sets the border property to a solid black border with a thickness of 2 pixels. We then set the border-radius property to 10 pixels, which creates a rounded border. Finally, we add some padding to the element to create some space between the text and the border.
Rounded Corners
In addition to creating a rounded border for an element, you can also specify the radius of each corner separately. This allows you to create unique shapes and designs for your borders.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Rounded Corners Example</title>
<style>
.rounded-corners {
border: 2px solid black;
border-top-left-radius: 50px;
border-top-right-radius: 10px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 10px;
border-bottom-right-radius: 50px;
padding: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="rounded-corners">
<h1>Hello, World!</h1>
<p>This is an example of rounded corners.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
A rendering of executing the code:

In this example, we have defined a CSS class called rounded-corners that sets the border property to a solid black border with a thickness of 2 pixels. We then set the border-top-left-radius property to 50 pixels, which creates a large rounded corner on the top left of the element. We set the border-top-right-radius property to 10 pixels, which creates a small rounded corner on the top right of the element. We set the border-bottom-left-radius property to 10 pixels, which creates a small rounded corner on the bottom left of the element. Finally, we set the border-bottom-right-radius property to 50 pixels, which creates a large rounded corner on the bottom right of the element.
Border Images
CSS border images allow developers to use images instead of solid colors for borders. This feature can add a unique look and feel to a website’s design. Border images are defined using the border-image property.
Understanding the Basics
The border-image property has five values:
source: Specifies the image URL to be used as the border.slice: Specifies how the image should be sliced into nine sections for border rendering.width: Specifies the width of the border.outset: Specifies the amount by which the border image area extends beyond the border box.repeat: Specifies how the image should be repeated to fill the border area.
Practical Example
Let’s take a look at an example that demonstrates how to use a border image.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Border Images Example</title>
<style>
.border-image {
border: 30px solid transparent;
padding: 15px;
border-image: url('border.png') 30 round;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="border-image">
<p>This div has a border image.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
A rendering of executing the code:

In this example, we have a div element with a class of border-image. We set the border property to a solid color of transparent with a width of 30px. We also set the padding property to 15px to create some space between the border and the content inside.
The border-image property is set to use an image called border.png as the border. We also set the slice value to 30, which tells the browser to slice the image into nine sections, and the repeat value to round, which tells the browser to repeat the image to fill the border area.
Explanation of the Code
The border-image property is a shorthand property that combines the border-image-source, border-image-slice, border-image-width, border-image-outset, and border-image-repeat properties into one.
The source value specifies the image URL to be used as the border. The slice value specifies how the image should be sliced into nine sections for border rendering. The width value specifies the width of the border. The outset value specifies the amount by which the border image area extends beyond the border box. The repeat value specifies how the image should be repeated to fill the border area.
In our example, we set the border-image property to use an image called border.png as the border. We also set the slice value to 30, which tells the browser to slice the image into nine sections. The width value is not specified, so it defaults to 1. The outset value is not specified, so it defaults to 0. The repeat value is set to round, which tells the browser to repeat the image to fill the border area.
By using a border image, we can create a unique border design that cannot be achieved with solid colors alone.
Multiple Borders
When it comes to creating intricate designs or emphasizing specific elements on a webpage, having multiple borders can be a powerful tool. CSS provides various techniques to achieve this effect, allowing developers to layer borders and create visually appealing layouts.
Border Stacking
One way to implement multiple borders is by stacking multiple elements with borders on top of each other. Each element can have its own border style, color, and width, allowing for a diverse range of designs.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Multiple Borders Example</title>
<style>
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 200px;
}
.box {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
border: 3px solid #f00;
border-radius: 10px;
}
.inner-box {
border: 3px dashed #00f;
border-radius: 8px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="box">
<div class="inner-box">
<!-- Content -->
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
A rendering of executing the code:
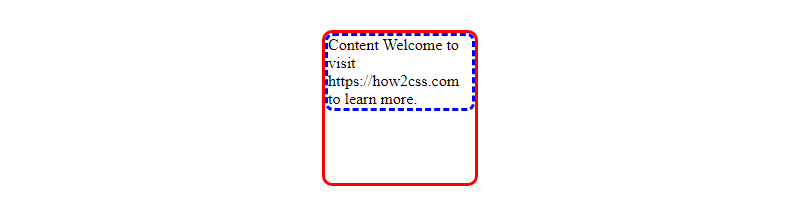
In this example, we have a container with a red solid border and a rounded border radius. Inside this container, there’s another box with a blue dashed border and a slightly smaller border radius. This creates a visually appealing effect with multiple borders.
Pseudo-Elements
Another approach to achieve multiple borders is by using pseudo-elements to create additional layers of borders around an element.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Multiple Borders Example</title>
<style>
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 200px;
position: relative;
}
.box {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
border: 3px solid #0f0;
border-radius: 10px;
}
.box::before {
content: '';
position: absolute;
top: -6px;
left: -6px;
width: calc(100% + 12px);
height: calc(100% + 12px);
border: 3px solid #00f;
border-radius: 15px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="box">
<!-- Content -->
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
A rendering of executing the code:

Here, we’ve added a pseudo-element ::before to the box element, creating an additional border layer around it. This pseudo-element has a green solid border and a larger border radius, giving the appearance of multiple borders around the box.
Border Shorthand
In CSS, you can use the border shorthand property to set all the border properties (i.e., border-width, border-style, and border-color) in one declaration. This can save you time and make your CSS code more concise.
The syntax for the border property is as follows:
border: border-width border-style border-color;
You can also specify just one or two values, and the missing values will be set to their default values (medium for border-width, none for border-style, and the current color for border-color).
Here’s an example:
.border-shorthand {
border: 2px solid red;
}
In this example, we set the border-width to 2px, the border-style to solid, and the border-color to red.
You can also use the border shorthand property to set different values for each side of an element’s border. Here’s an example:
.border-sides {
border: 2px solid;
border-top-color: red;
border-right-color: blue;
border-bottom-color: green;
border-left-color: yellow;
}
In this example, we set the border-width to 2px and the border-style to solid. Then, we set the border-color for each side of the element separately.
You can also use the border shorthand property to set different values for the horizontal and vertical borders of an element. Here’s an example:
.border-hv {
border: 2px solid;
border-color: red green;
}
In this example, we set the border-width to 2px and the border-style to solid. Then, we set the border-color for the horizontal and vertical borders separately.
Overall, the border shorthand property is a useful tool for setting border properties quickly and concisely. Just remember to follow the correct syntax and order of values.
 How CSS
How CSS